Periodontology
Periodontology can also be known as Periodontics, the specialty practice of dentistry in preventing, diagnosing, and treating diseases affecting the supporting structures of the teeth. These consist of the periodontium, which is defined to include the gingiva, alveolar bone, cementum, and periodontal ligament. Adequate health of the tissues can ensure an adequate set of teeth and enable one to avoid most diseases that most often result in tooth loss or even systemic diseases.
The word "Periodontology" is derived from the Greek words peri, which means "around," and odons, which means "tooth." Periodontology is the science of the study and care of the tissues "around the tooth" that support, stabilise, and nourish each tooth.
The Structures of the Periodontium
There are four main structures in the periodontium, all playing critical roles:
Gingiva: Gingiva is the soft tissues around the teeth. Healthy gingiva are firm, pink, and snugly fitted around each tooth, protecting the teeth from bacteria invasion. They prevent infection from getting deeper into the tissues of the bone and roots. When the gums become inflamed due to bacterial build-up, a condition called gingivitis can develop and may cause redness, swelling, and bleeding. Gingivitis is the initial stage of periodontal disease and, if left untreated, can lead to serious conditions such as periodontitis.
Alveolar Bone: These are the sockets used to anchor the teeth. This bone gives solidity and strength to the teeth, which then maintains its position and will be able to withstand forces exerted during biting and chewing. As periodontal disease progresses, it destroys the alveolar bone; this causes loosening of the teeth and eventually loss. The alveolar bone must be protected for proper, long-term dental health.
Cementum: The cementum is a calcified layer that covers the root of each tooth and assists in the anchorage of the tooth within the jawbone. Cementum allows the periodontal ligament to securely anchor itself to the tooth root. Cementum also grows in size throughout one's lifetime and can assist with replacing some of the worn surfaces on the teeth naturally due to erosion. Destruction of or infection of the cementum may cause loosening or loss of the involved tooth.
Periodontal Ligament: The periodontal ligament is formed of connective tissue fibres connecting each tooth root to the alveolar bone around them. This ligament is a shock absorber in that it softens the impact on teeth in forces that occur during biting and chewing. This little elasticity also allows for equal pressure distribution to keep the bone and teeth healthy.
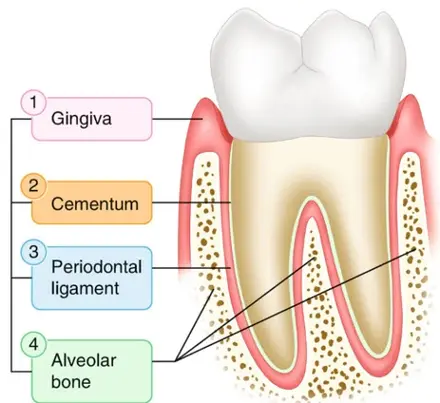
Image source: https://media.springernature.com/lw685/springer-static/image/chp%3A10.1007%2F978-3-031-38567-4_3/MediaObjects/503767_1_En_3_Fig1_HTML.png
Common Periodontal Diseases and Conditions
These diseases of the periodontium are more commonly known as periodontal diseases, and consist of gingivitis and periodontitis. The causes of these diseases are often bacterial infections, resulting from plaque buildup on the teeth. When plaque is not removed properly, it dries into tartar, a substance that can only be removed with professional cleaning. Periodontal disease usually progresses through these stages:
Gingivitis: This is the first stage of periodontal disease. Gums become red, inflamed, and easy to bleed. Gingivitis is most often the result of poor oral hygiene resulting in plaque along the gumline. It can be reversed with professional treatment and improved at-home oral care.
Periodontitis: If gingivitis is not treated, then it may progress into the more destructive and serious type of gum disease, called periodontitis. The condition is characterised by formation of "pockets" in between the teeth and the gums. Bacteria and plaque accumulate in such a pocket, leading to breakdown of the supporting tissues and bone. This causes movement of the tooth and its subsequent loss if not treated in time.
Advanced Periodontitis: In the most severe stage, periodontitis can cause massive bone loss, gum recession, and even widespread tooth loss. In such a case, treatment may be more complex and involve bone grafting or surgery.
Periodontal Treatment Options
We at Ginza Dental Surgery, dentist at Clementi, offer a range of periodontal treatments tailored to each patient's needs
Scaling and root planing: This is a procedure which does not require surgical methods. Scaling removes the plague and tartar off from the surface of the teeth mainly below the gum-line. Root planing gives an even surface of the roots of the teeth where again bacteria cannot bind itself with the gums. After performing this procedure, there would be a decrease in the inflammation and gums are enabled to heal and adhere with the teeth.
Antibiotic therapy: If the infection is in the gums, antibiotics are prescribed to reduce bacteria and heal. Antibiotics may be used in combination with scaling and root planing for maximum effect.
Gum Surgery: Advanced periodontal disease is often treated with surgery. Gingival flap surgery includes lifting the gums to eliminate tartar lodged deep within them and then repositioning the gums to snuggly fit around the teeth. Bone or tissue grafting may be needed if there has been major loss of bone or tissue.
Maintenance Care: Following the active treatment, periodontal maintenance is important to avoid recurrence. Routine checkups and professional cleanings are important to maintain healthy periodontium and to monitor signs of gum disease.
Why Choose Us
The preservation of health periodontium is the only way to have well-preserved teeth as well as good health preservation. Periodontal diseases have been linked to many other systemic conditions, including heart problems, diabetes, and respiration disorders. Avoidance of bacteria in the bloodstream and improvement in health depends on healthy gums.
At Ginza Dental Surgery, we are the best dentist near Clementi. We focus on early diagnosis, personalised treatment, and preventive education in periodontal care to enable our patients to maintain a healthy and beautiful smile.
Address Information
Ginza Dental Surgery
Blk 612 Clementi West St. 1, #01-302,
Singapore 120612
Tel: 6774 4901
Fax: 6773 2175
Operating Hours/Opening Days
For Appointment, please call
6774 4901
Monday to Friday (星期一至星期五)
9.30am - 12.30pm
2pm - 5pm
Saturday (星期六)
9.30am - 12.30pm
2:00pm - 4.30pm
Monday and Wednesday night (星期一及星期三晚上)
7:00pm - 9:00pm
Friday evening (星期五傍晚)
5.00pm - 7.00pm
Sunday & Public Holiday (星期日及公眾假期休息)
Closed
